Detailed building facts
On this page we describe the building facts in a more detailed manner, presenting the various features in the lab and common areas.
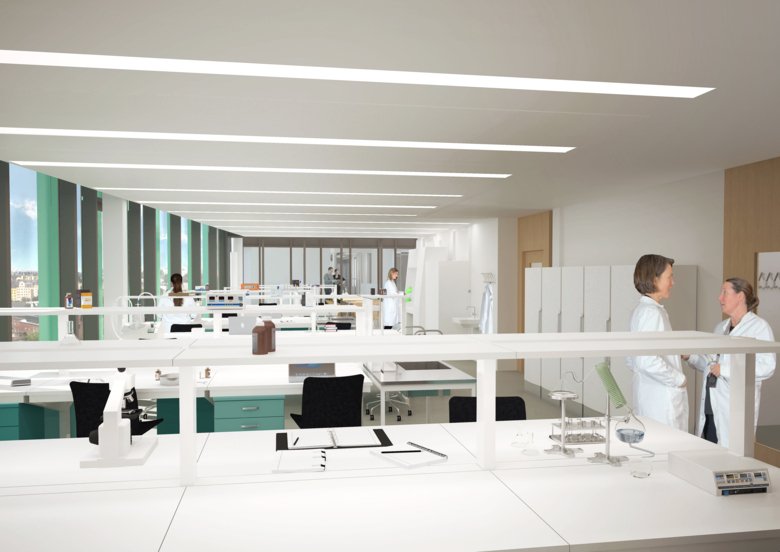

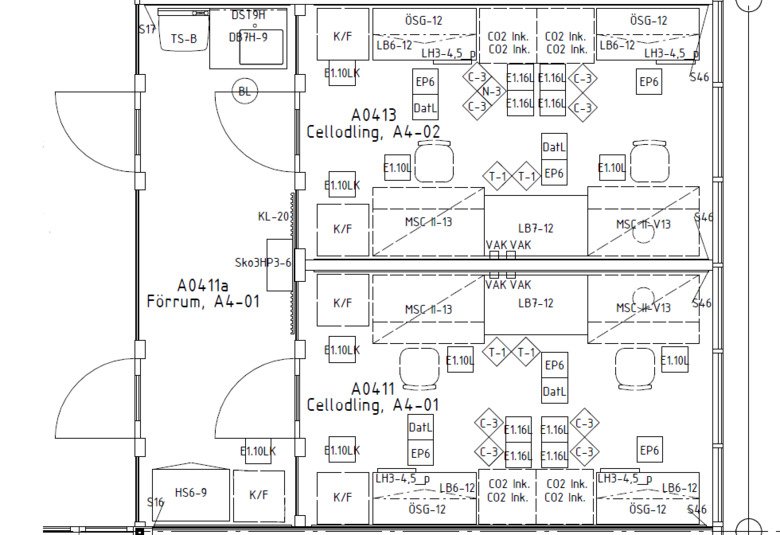
Open general lab
The underlying idea of open labs is to support group-based work and they are open towards lab corridors. In open labs, researchers are expected to share equipment, bench space, and support functions such as storage and services. Open labs are designed to facilitate communication between scientists and make the labs more easily adaptable for future needs. Closed labs are available for specific types of research or for specialized equipment.
Features
- Rooms and installations have been adapted to the users’ needs.
- Laboratory modules, equipment and furnishings are easy to relocate based on specific needs of the researchers.
- Furnishings decided upon in close cooperation with researchers.
- Wall-mounted lab furnishings make the space feel open and airy as well as easier to keep clean.
- Easy access to nearby offices.
- Functional area around individual workstations is carefully designed to effectively supply various media (e.g. compressed air, gases or cold water) needed for everyday use.
- Media pipes are fed from the ceiling and the piping has been partially concealed for aesthetic reasons, while still affording access for cleaning and repairs.
- Lighting has a motion control and an on/off button. Motion detectors switch off lighting after 15 minutes if no movement is detected.
Regular tissue culture room
Features
- The ventilation is equipped with a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter in order to ensure a clean environment.
- Tissue culture rooms have, by default, a slightly positive pressure to keep outside untreated air from seeping in. The pressure can be changed to slightly negative if requested.
- An air cooler is installed in the ceiling to maintain the temperature at comfortable level.
- The cell culture room can be equipped with two biological safety cabinets, of which one can be connected to the facility exhaust system.
- The room is supplied with compressed air and CO2 gas.
- Sink and hand washing units are placed in the anteroom.
- The laboratory is designed according to Biosafety Level 2.
- Light has absence control and an on/off button. Presence detectors switch off light after 15 minutes if no presence is detected.
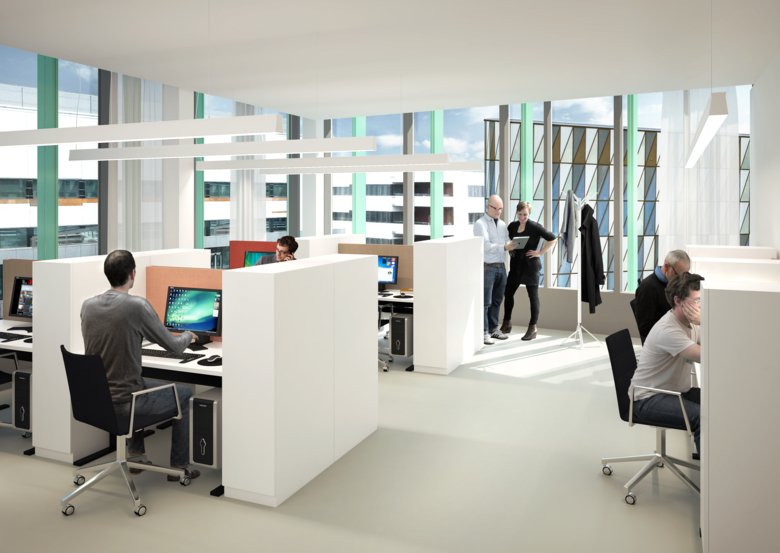

Offices
Biomedicum will contain a variation of one-person offices and open plan offices. In the mockup house a typical lab quarter set-up can be seen - a one-person office and eight open workstations, which is the maximum number decided upon.
Desks have been designed so as to create functional, uniform and space-efficient workstations for 1,600 people. All desks are height-adjustable and each has its own lockable safe and a new chair.
Windows facing the exterior have indoor curtains, with centrally controlled louvered blinds on the outside in order to maintain interior climate.
Ceilings
Each storey of Biomedicum is 3.9 m high. Taking this and the large number of installations required by a modern laboratory into account, the labs have a free ceiling height of 2.7 m. In most offices, however, it will be 3.1 m.
Rubber floor covering
The flooring chosen for the building is of the same kind as that in the Retzius lab and similar spaces. It has a rubber floor covering that is very well suited to the lab environment. The colour has been decided by the architect, but Karolinska Institutet has been involved in the decision that it is to be plain (i.e. without pattern) to make it easier to locate small items if dropped. The floor covering is normally 2 mm thick. In the office sections, a 3 mm-thick covering has been chosen to achieve an optimal acoustic environment.
Common spaces
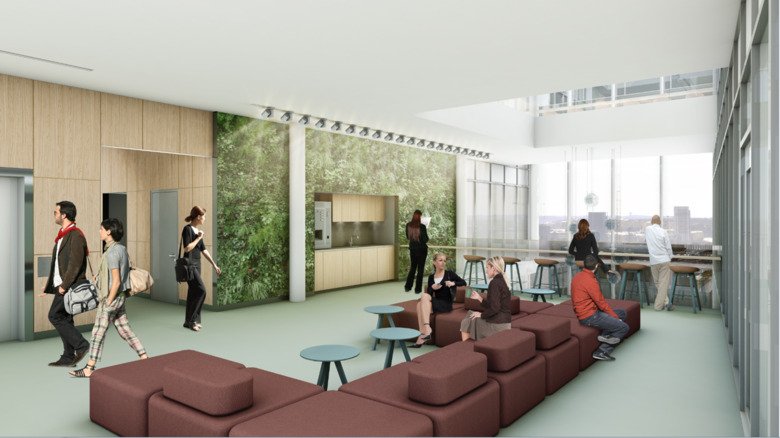

Biomedicum is designed with the aim of creating a flexible, accessible and functional working environment with plenty of natural meeting places to promote exchanging of ideas and experiences, and foster collaboration.
Common spaces on all floors support creativity and informal meetings. The building facilitates interaction between researchers from different departments, and generates opportunities for dynamic and continuous changes in the group compositions as it will be easy to relocate within the building. This fosters a creative atmosphere. Facilities for scientific teaching, presentations and education will also promote close interaction between students and researchers.
Meeting places in the slits
Between the four sections of Biomedicum there are so called “slits” on floor 3-10. There are three types of slits, all of them are prepared for coffee stations and various types of furnishing due to the available space. The idea is that the slits, some with adjacent bookable meeting rooms, will become natural meeting places, both official and unofficial, planned or spontaneous, and open to all personnel.
In the large slits interactive activities and open meetings can be held. Smaller slits can be used for more personal and informal meetings, telephone calls or undisturbed work.
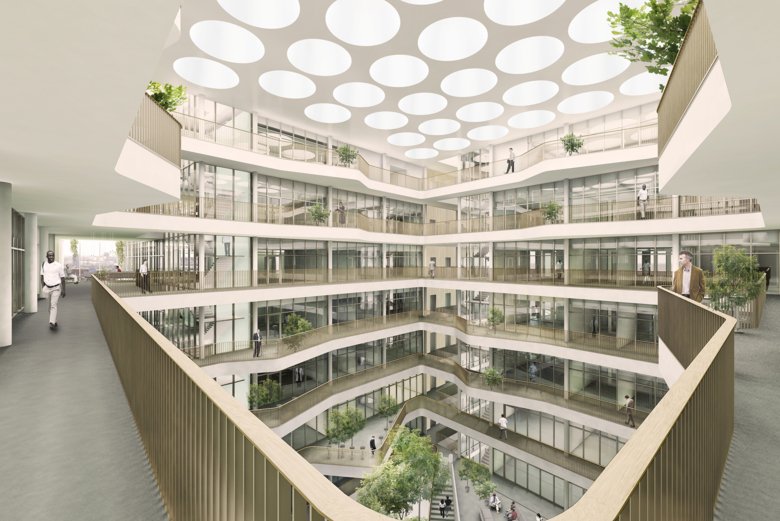
The atrium
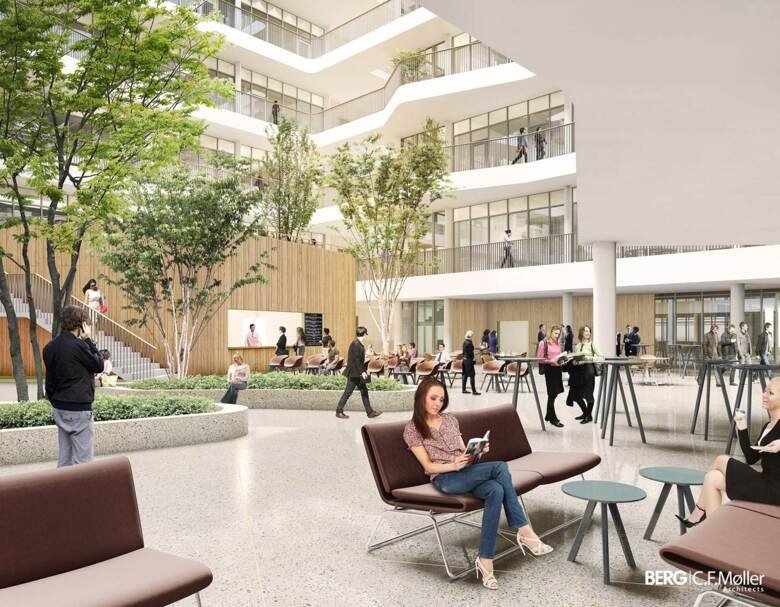

The atrium on the entrance floor (3) is considered a common space area with reception, café, mingling area, conference rooms and entrance to the auditorium. It is an area open to the public.
Thanks to large glass walls facing a centrally placed atrium rising from level 3 to level 10, activities in different parts of the building will be made visible to all colleagues. The atrium will also contain vegetation, with the intention that it will be like a small park.
Several different kinds of material have been tested for the suspended ceiling under the balconies. One requirement has been to keep the sound environment, which is an important function for the atrium, at “an acceptable level” of noise without the disturbing clatter of cutlery from the café and eating spaces, but high enough for people to hold private conversations without overhearing others.

Faculty club and lunch seats
There will be a faculty club on floor 10 which can accommodate about 75 seats, and there will be lunch rooms on the 4th and 10th floor which can accommodate about 400 seats.
Accessibility
Accessibility needs have been observed throughout the Biomedicum project. The aim is to create optimal accessibility for all general areas, laboratories and offices, ensuring that people with disabilities and reduced mobility not only enjoy freedom of movement to, into and within the building and use of its facilities, but also can reach safety in the event of fire or other emergency.
Examples of accessibility measures applied at Biomedicum:
- Choice of non-allergenic plants at the entrance and in rooms.
- Simple, logical room layouts.
- Consistently located structural components, fixtures and fittings.
- Marked obstacles, contrast markings and signage.
- Wheelchair access to auditorium for speakers and audience, and to conference rooms.
- Avoidance of high-gloss surfaces and glossy paints that can cause disturbing glare or reflections.
- Staff kitchenettes that can be used by people with reduced mobility or orientation.
- Easily reachable cupboards, coffee machines and microwaves.
- Good acoustics that allow people with impaired vision to judge the layout of a space and to identify sounds.
Accessible workspaces
Offices, general labs, common spaces, lavatories, refectory, faculty club, conference, meeting rooms, lab shop, bicycle storage room, changing rooms.
Specialist lab (For example tissue culture room)
Where there is more than one specialist lab of the same type on one floor, KI deems that the work can be done if at least one of the labs has wheelchair access.
Some areas will not be accessible to everyone owing to the nature of the work carried out.
Office ventilation, climate & light
Ventilation and climate
The office sections are ventilated through a ventilation terminal in the ceiling. It has a built-in cooling mechanism that lowers the supply air temperature on hot days or when the office space is crowded. It is controlled automatically to maintain the temperature selected for the whole area.
The ventilation and cooling systems are interlocked so that the radiators (hot water central heating) do not heat the space at the same time as the baffles cool the incoming air.
The office space ventilation is shut down in the evenings and at weekends, although there is an override button at the entrance to the block that turns it back on for an hour or so. The conference room ventilation has an override button that increases the flow of air and allows the ventilation system to be switched on during the evening.
Light controls
Open plan offices with 8 workstations:
- Individual control of downward lighting at each workstation/desk. Luminaires are fitted with presence detectors.
- Day (7.00 am – 7.00 pm): Uplight from luminaires is controlled via a timer channel.
- Night (7.00 pm – 7.00 am): Uplight from luminaires is controlled/switched on via presence detectors fitted in the ceilings and switched off again after 15 minutes if no further presence is detected.
- The light fitting schedule is to include ceiling mounting rails so that adjustments can be made for workstations.
One-person offices:
- Individual control by workstation/desk. Manual on/off switch.
- Pendant luminaires above desks are controlled via a pull dim-switch for up/down light.
- Controlled by an integrated presence detector in the luminaire.
- Buttons by doors turn on/off general lighting (needed owing to size of room).
Solar blinds
Biomedicum has two types of solar blinds, textile and metal. All solar blinds are controlled automatically, which is necessary for maintaining the interior climate and the building’s energy efficiency.
Blinds are centrally controlled to be lowered and angled when, where and to the extent necessary. Blinds will not be lowered for rooms in shade or when it is overcast. Blinds are controlled per room or, for large rooms (e.g. extending along an entire façade) in logical sections. In some rooms (e.g. conference rooms) it will be possible to lower blinds even when this is unnecessary in terms of interior climate and energy efficiency.
Textile blinds are made of material of approx. 5 – 10 per cent transparency, allowing shapes and light/shade (perhaps more) to be visible through them at close range. From the outside, they reflect light and appear opaque.
The metal blinds are either fully retracted or fully lowered, and when lowered will be angled to the necessary degree (usually less than 30 degrees, which makes it possible to see out of the window). In the spring (March-April) when the sun is bright and low and on early summer mornings (and perhaps later afternoons) the blinds will be angled at more than 30 degrees.
Energy and environmental targets
Karolinska Institutet and Akademiska Hus have drawn up a joint environmental programme for the construction of Biomedicum in order to meet the established energy and environmental targets needed to obtain a Silver Energy and Environmental Design certificate.
Certification will be awarded on completion of the building, and involve the control and follow-up of 16 indicators in the fields of energy, interior environment and material.
The green sedum roof contributes to rainwater management, and parts of the roof have been designed to accept solar panels. Biomedicum shares a power plant with a nearby building and part of the energy comes from thermal boreholes between the buildings.
The project team members have made considerable efforts to create a building that allows efficient and secure ways of managing inflows of people and materials such as waste or consumables.
