Waste Management in Biomedicum
Correct sorting of waste is important. By following the waste routines, the risk of incidents is minimized, and the work environment improved. Recycling materials also reduce our environmental impact.
Below handling instructions of the most common waste types at Biomedicum are summarized.
1. Recyclable Waste
In Biomedicum there is one main recycling room as well as local recycling rooms in all quarters.
Main Recycle Room
The main recycling room in Biomedicum is located on floor 2 (room G0203).
Available recycling fractions
- Paper packaging
- Plastics
- Soft plastics
- Metal/metal packaging
- Small batteries
- Electronics
- Light sourses
- Flourescent tubes
- Uncolored glass
- Colored glass
- Styrofoam
- Confidential waste
- Corrugated cardboard
- Waste (combustible)
- Other waste
- Return bottles
Opening hours for the main recycle room
Monday-Friday: 07:30 –16:00
Recycle Rooms in Quarters
In addition there are local recycle rooms in each quarter in Biomedicum.
Available recycling fractions:
- Paper packaging
- Plastic packaging
- Metal packaging
- Small batteries
- Electronics
- Light sourses
- Uncolored glass
- Colored glass
- Styrofoam
- Corrugated cardboard
- Other waste
In the recycling rooms also these fractions are placed for collection:
- Sharp/infectious waste/yellow box
- Pharmaceutical waste/yellow box
- Dirty labware
- Laundry/Dirty lab coats
The recycling containers are emptied daily by FM personnel and transported to the main recycling room.
Do not discard any chemicals, infectious material, or sharp objects (e.g. broken glass) in the recycling fractions. These should be disposed of as hazardous laboratory waste.
If you have spare clean dry ice from e.g. deliveries, please empty this to the dry ice boxes on floor 2 instead of letting it evaporate in the recycling room. Use the fume hoods if evaporation of dry ice is needed.
Trolleys
For easier handling of recyclable waste in the lab you can use a trolley with the possibility to recycle up to four different fractions of your own choice.
When full, please empty the containers in the correct fraction in the main recycle room on floor 2.
Use KI:s waste signs for correct labeling of your containers.

2. Hazardous Waste
The following apply for all hazardous waste:
- The waste bins must not weigh more than 12 kg. Do not overfill the containers.
- The outside of the containers must be clean and safe to handle for the personnel taking care of the waste.
- The container must be correctly labelled and the label completely filled in.
- Liquid waste should always be contained in a container/bottle with a tight lid. Choose proper type of container according to the liquid and its chemical properties.
- Unmarked or wrongly handled waste will not be collected by the FM personnel and will be labelled with the "Incorrectly prepared waste containers"-label showned below. Remove the label when attended, and FM will collect the waste.
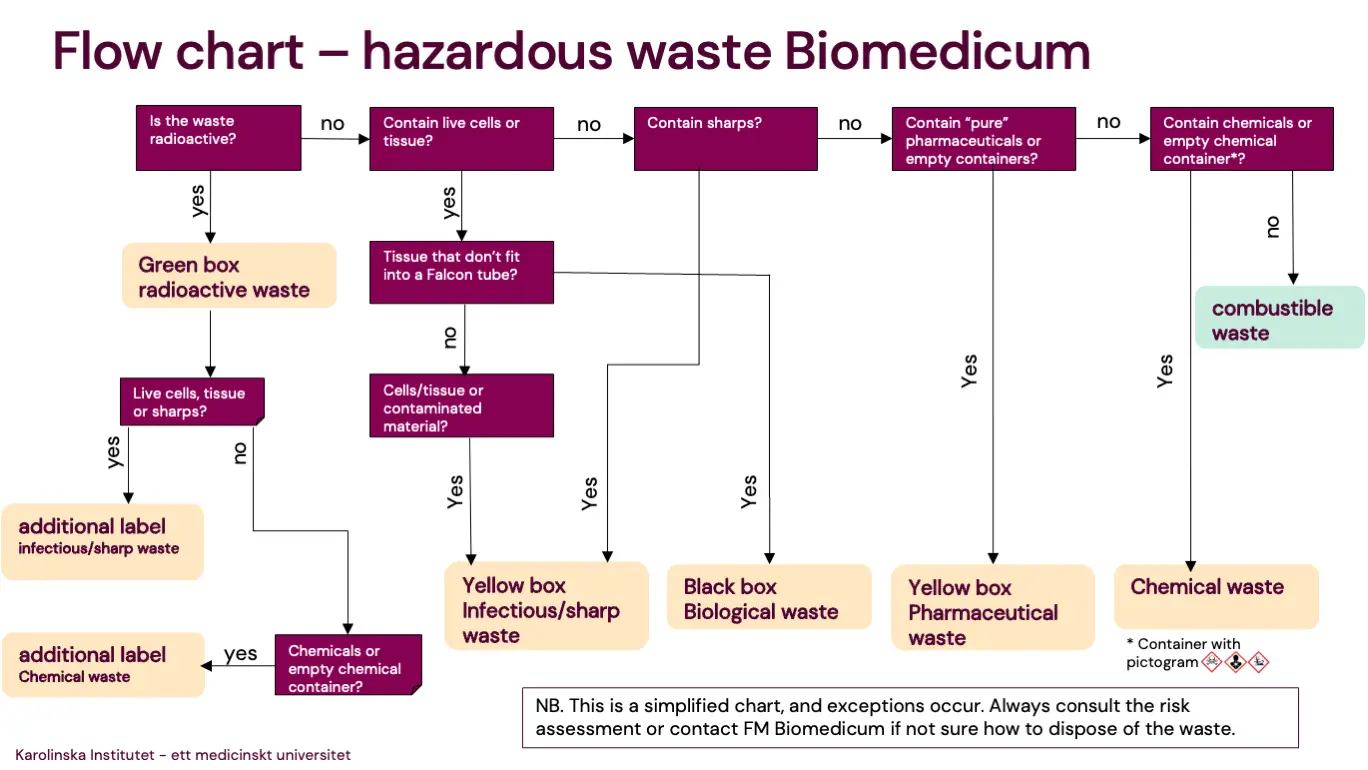
2.1 Sharp and Infectious Waste
Sharp and infectious waste should be disposed of in a yellow box and marked with the sharp/infectious sticker as the box is taken into use. Labels “Skärande/stickande smittförande” and yellow waste boxes are available in the clean glassware rooms on floor 4–9. Correctly labeled and closed yellow box should be placed in the quarter recycling room for pick up by FM personnel.
Sharp waste includes all sharp objects such as needles, scalpels, lancets, suture needles, microscope slides and broken glassware. This applies even if the material is not suspected to be infectious, is unused, or if contaminated with biological or chemical contaminants.
Infectious waste includes for example human blood and blood products, micro-organisms, cell cultures, and materials that have come into contact with these waste types, for example gloves, inoculation loops, pipette-tips, pipettes, tubes, paper towels.
Plastic pipettes and pipette tips are a special type of pseudo-sharp since they can puncture or cut under special circumstances. If non-contaminated, plastic pipettes and pipette tips may be disposed of as recyclable or household waste. Pipettes and tips must then be properly contained first, for example in a plastic bag, in order not to be able to cause any punctures/cuts.
2.1.1 Solid Waste
- Sharp and/or infectious solid waste must be collected and placed in a yellow box.
- If the smaller sharp/infectious containers with red lids are used, put these when full into a larger yellow waste box (30L or 60L).
- Contact FM if you need to autoclave your waste.
2.1.2 Liquid Waste
- Infectious liquid waste must first be collected in leak-proof sealable bottles or containers, and then placed in a yellow box. Note that the box should not weigh more than 12 kg.
Small amounts of antibiotics/cytostatic/chemicals are often used in combination with infectious agents. This mixed waste should always be handled as sharp and infectious waste.
2.2 Pharmaceutical Waste, Including Cytostatic Waste
Pharmaceutical waste includes antibiotics, hormone preparations and cytostatics, vaccines, narcotic drugs and objects that come into contact with these materials, for example packaging that contained antibiotics, cytostatics or other pharmaceuticals.
Yellow waste boxes and labels “Cytostatika och läkemedelsförorenat avfall” and “Hazardous to environment” are available in the room for clean lab glassware on floor 4-9. Label the box when start being used. When full, the correctly labeled (NB two stickers should be used) and closed yellow box is placed in the quarter recycling room for pick up by FM personnel.
2.2.1 Solid Waste
Waste that has been contaminated with cytostatic and other pharmaceuticals must first be placed in a sealed inner packaging (sealed plastic bag or similar) and then placed in a yellow box.
2.2.2 Liquid Waste
Liquid pharmaceutical waste must first be collected in leak-proof sealable bottles or containers, and then placed in a yellow box.
- Needles and other sharp waste contaminated with cytostatics should be handled as “Sharp and infectious” waste.
- Narcotic substances are subjected to additional regulations, for more information contact your group leader or FM helpdesk.
2.3 Biological Waste
Biological waste includes human- and animal body parts, carcass, tissues, teeth and organs, as well as anatomical preparations and similar.
Black waste boxes labeled with “Biologiskt avfall” can be ordered via FM Helpdesk . Label the black box, fill the box with bagged material and bring the black box to the freezer room at floor 2.
Contact FM Helpdesk for room number and access.
- Biological waste must always be stored frozen. Store biological waste in sealed bags in a freezer in your lab until you have enough material to fill a container.
- Biological waste should only be transported outside the lab in the black box.
- The material must be placed in plastic bags before placing it in the container. Absorbents should be placed in the bottom.
- Sharp waste (e.g. tissue slides, needles) and cultures with cells or microorganisms (contaminated with biological material), human blood and blood products, as well as material contaminated by these, is handled as “Sharp and infectious” waste. All consumables that come into contact with biological material can be handles as “Sharp and infectious” waste.
- Smaller organs etc. from animals prepared in eg 15 or 50mL tubes should be handled as “Sharp and infectious” waste.
2.4 Chemical Waste
All chemical waste should be handled, packaged and labelled according to Karolinska Institute’s rules for laboratory waste management. For a summary of the waste routines, please see below.
Note that it is important to store the chemical waste according to the properties of the chemical itself. For example, flammable waste must be stored in an fire safety cabinet and separated from other chemicals. N.B.: only flammable chemicals should be stored in the fire safety cabinet. Consult Karolinska Institute´s rules for chemical storage. More information regarding management of a specific chemical product can also be found in KLARA, the chemical database.
2.4.1 Chemical Waste Includes
- Chemicals marked with hazard symbols including reagent solutions, solvents, oils, paints, adhesives, disinfectants, etc.
- Unidentified chemicals (must be denoted with “Unknown chemical”).
- Materials such as gloves, paper towels and test tubes, that are contaminated with chemicals labelled with the hazard symbol for “Highly toxic”, “Carcinogenic/Mutagenic” and/or “Environmentally toxic”.
- Bottles and cans labelled with the symbol for “Highly toxic”, “Carcinogenic/Mutagenic” and/or “Environmentally toxic”. This also applies to empty containers.
- Photochemical waste; developers, scintillation fluid, fixing solutions and films.
- Certain objects containing environmentally hazardous metals such as mercury thermometers and lead aprons from radiography.
2.4.2 Routine for Chemical Waste Collection
Place chemical waste in the ventilated- or fire safety cabinets collection spot in the niche next to the entrance to the quarter. FM goods & logistics will collect the waste regularly.
Place the flammable chemicals in the fire safety cabinet, and the rest of the chemicals in the ventilated cabinet. Do not store incompatible chemicals together.
In case of uncertainty about storage, read the safety data sheet for the chemical or contact FM helpdesk.
Only chemicals ready to be collected can be stored in the waste cabinets.
Incorrectly labeled or incorrectly closed chemical waste containers will not be collected.
Empty bottles or chemicals in the original container does not need the chemical waste sticker. Please note that chemical glass-containers should not go to glass recycling.
Alternatively
Send a ticket to FM helpdesk and FM will arrange a pick-up from your laboratory. Please note that the chemical waste needs to be stored in ventilated or fire safety cabinets until pick-up.
2.4.3 Labeling
Use the “Chemical waste” label directly on the container/the bucket or cardboard box. The container must be marked with the content, date, dispatcher, and department affiliation, and the correct pictogram should be crossed.
Labels and empty containers for chemical waste are available in room for clean lab glassware on floor 4-9. Cardboard boxes (including black bag and cable ties) for chemical waste are available in the recycling rooms in each quarter.
Unmarked or wrongly handled waste will not be collected by the FM personnel and will be labelled with the "Incorrectly prepared waste containers"-label showned below. Remove the label when attended, and FM will collect the waste.
2.4.4 Solid Chemical Waste
Solid chemical waste should be disposed of in its original packaging or other suitable material – preferably the same type of material that the chemical was originally stored in. Never mix chemicals of different types. The container must be properly sealed, clean on the outside and the lid must be intact.
Chemical waste mixed with contaminated consumables can be placed in a white bucket for chemical waste, or in the cardboard boxes (with thick black bags) for chemical waste.
- Sharps contaminated with chemicals should always be placed in the yellow box for “sharp and infectious” waste.
- Contaminated consumables, such as pipette tips, plastic tubes or similar, that have been in contact with chemicals that are not labelled with the hazard symbol for “Highly toxic”, “Carcinogenic/Mutagenic” or “Environmentally toxic” can be placed in a sealed inner bag and then handled as recyclable waste, that is, sorted according to content, e.g. “plastic waste”, ”combustible waste” etc.
2.4.5 Liquid Chemical Waste
Liquid chemical waste should be poured into a suitable container (glass bottle/plastic bottle/container etc.) – preferably into a container of the same type of material that the chemical was originally stored in. The can or bottle must not be affected by the contents.
Please note that buckets or similar containers should not be used for liquid waste, the lids are not tight enough.
Never mix chemical liquids of different types. Some liquid chemicals such as for example some buffer solutions can be mixed but verify this before you combine them by reading the Safety Data Sheets of the chemicals.
The container must be properly sealed, and the lid must be intact. The container must be clean on the outside and safe to handle.
2.4.6 Empty Chemical Bottles/containers
Empty bottles and cans labelled with the following hazard symbols for “Toxic”, “Serious Health Hazard” and/or “Environmentally toxic” must always be handled as chemical waste.

Dispose these the same way as liquid chemical waste, but original containers do not need a waste sticker.
Clean and decontaminated packaging that do not have the above hazard symbols can be handled as recyclable waste, i.e. sorted as glass, hard plastics, etc. NB, remove all the hazard labels before placing the container in the recycling bins.
Packaging and bottles that has contained flammable goods must be opened and rinsed carefully before the packaging/bottles are placed in the recycling bins.
In cases of doubt, bottles shall be handled as chemical waste.
- Disposing chemicals that have hazard statements and hazard pictograms down the sink is forbidden! For more information see Karolinska Institute’s rules for laboratory waste management.
- Nutrient solutions that only contain vitamins, electrolytes, amino acids, peptides, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids are not considered to result in any significant effects on the environment. Residues from such nutrient solutions can be poured into the drains.
2.5 Radioactive Waste
Work and research involving radiation at KI is required to be according to Swedish law and regulations. Information on isotope work at KI is found at the radiation protection webpage.
All radioactive waste must be placed in a green box and never be disposed of with other waste. FM Biomedicum collects all the radioactive waste, registers it, and calculates the activity to determine the time when it can be sent for destruction.
2.5.1 General instructions
- Use a green box and fill out the label for radioactive waste. Boxes and labels are found in the isotope labs.
- Liquid waste must always be poured into, for example, a plastic container sealed with a tight lid before being placed in the box.
- Always separate different isotopes; when this is not possible, state the estimated activity for each isotope.
- See section 2.5.2 for information about additional labels required when the box also contains chemicals or scintillation fluid.
- See section 2.5.3 for information about additional labels required when the box also contains infectious waste.
- When the box is full, ensure all labels are correctly completed and send a ticket to FM Helpdesk for collection.
- Please send a ticket to FM Helpdesk when containers or labels are out of stock.
2.5.2 Radioactive Chemical/noninfectious Waste
Scintillation fluid should be separated from other radioactive waste. Sort scintillation waste separately and label the box with the label “Chemical waste scintillation fluid” as well as the radioactive waste label.
Chemical waste stickers are available in the clean glass rooms on floor 4-9.
2.5.3 Radioactive infectious waste
Radioactive infectious waste must, in addition to the radioactive waste label, be marked with the “Skärande/stickande smittförande” label.
“Skärande/stickande smittförande” labels are found in the rooms for clean glassware on floors 4-9.
3. Empty Gas Tubes
All quarters have a designated gas storage room, and empty bottles should be stored here. Always keep gas tubes chained, also when empty. Keep full and empty tubes separate.
Do not store incompatible gas containers together, e.g., flammable and oxidizing gases.
Empty gas tubes will be transported to floor 2 by FM personnel. Contact FM Helpdesk.
Empty small camping gas containers can be placed in the fire safety cabinet shelf for chemical waste for pick up by FM.
4. Laboratory Equipment Waste
Excess functional equipment should first and foremost be used within KI. Hence, publish information about your excess equipment on Buy and sell on the Staff portal. Fill in and send the form I have lab equipment to sell/give away.
Please follow the guideline for laboratory move or termination for equipment that is useless and without value and should be discarded. The objects need to be cleaned and decontaminated before transport. A decontamination waste label must be filled in and placed on the object.
Contact FM Helpdesk for assistance with transport to the recycling room at floor 2. Please note that equipment without correct labelling will not be handled by FM.
Contact
If you have any questions please contact the FM Helpdesk
